Texture vs. Taste: How Food Consistency Triggers Acid Reflux
Understand endoscopic surgery: what it entails, the procedure, benefits, and...
GERD is a common digestive condition that affects many people, and can have long-term health implications if not treated properly. It occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which connects the stomach to the esophagus, becomes weak or relaxed and allows stomach acid to travel back up into the esophagus. This can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms, such as heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), coughing, shortness of breath and chest pain. Some people may even experience esophageal cancer due to prolonged GERD.

Common symptoms of GERD can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as:
Other symptoms of GERD include nausea, sore throat, hoarseness, wheezing, teeth erosion, ear infections and severe pain which can sometimes be mistaken as a heart attack. Some people may even experience esophageal cancer due to prolonged GERD.
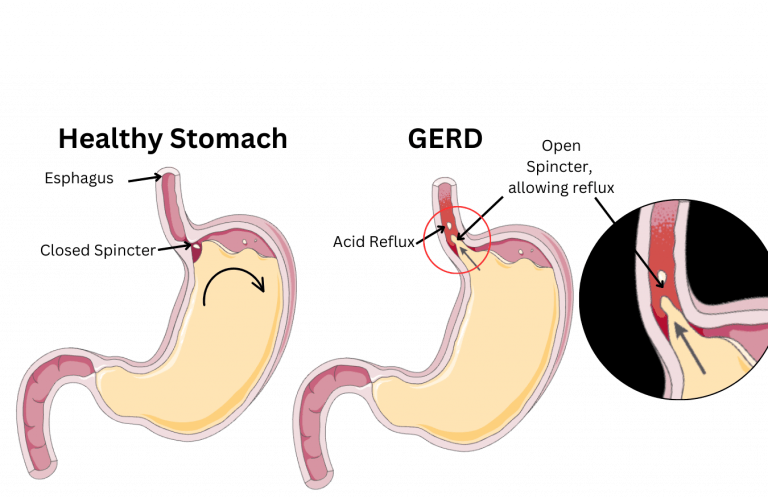
Gerd causes the following:
Yes, GERD can cause shortness of breath when stomach acid irritates the esophagus and triggers airway inflammation. This can lead to breathing difficulties, trigger asthmatic reaction or cause wheezing, and chronic coughing. If you experience persistent shortness of breath along with acid reflux, it may be a sign that GERD is affecting your respiratory system. Seeking proper treatment can help manage both acid reflux and breathing issues effectively.
Other symptoms of GERD include swallowing difficulty, nausea, cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, hoarseness, wheezing, teeth erosion, ear infections and severe pain which can sometimes be mistaken as a heart attack.
GERD has four stages, depending on the severity and frequency of symptoms:
Stage 1:
Occasional Symptoms – Mild heartburn or acid reflux that occurs less than twice a week.
Stage 2:
Frequent Symptoms – Heartburn or acid reflux that occurs more than twice a week, but not every day.
Stage 3:
Chronic Symptoms – Persistent heartburn or acid reflux that occurs every day and requires medication for relief.
Stage 4:
Complications – Long-term damage caused by GERD such as strictures (narrowing) in the esophagus, Barrett’s esophagus (abnormal cells in the esophagus), and esophageal cancer.
GERD can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your doctor may review your symptoms, ask about your diet and lifestyle habits, and perform a physical exam to check for any signs of GERD.
Additionally, your doctor may recommend certain tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. These tests may include:
Treatment for GERD will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the stage of your condition. Some treatment options include:
If medications fail to treat GERD, surgery may be recommended by the doctor.
In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to strengthen the LES or repair any structural issues that contribute to GERD.
It’s important to consult with a doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of GERD, as early diagnosis and GERD treatment can prevent long-term complications.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a common digestive disorder that affects many people in Singapore. It occurs when the stomach acid and other contents flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. While GERD can be managed with proper treatment, it can also lead to complications if left untreated.
Here are some of the potential complications of GERD in Singapore:
Esophagitis is inflammation or irritation of the lining of the esophagus, which can occur due to prolonged exposure to stomach acid from GERD. This condition may cause symptoms like difficulty swallowing, chest pain, or heartburn. If left untreated, esophagitis can lead to more serious complications such as esophageal ulcers or strictures.
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus change and become like those found in the intestines. It is often caused by long-term GERD and can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. Regular monitoring and treatment are essential for managing Barrett’s esophagus.
GERD can also cause or worsen respiratory problems, such as asthma, chronic cough, or hoarseness. This is because stomach acid can irritate the throat and lungs when refluxed. Treating GERD can help improve these symptoms.
Stomach acid from frequent acid reflux can also damage tooth enamel, leading to dental complications such as erosion, discoloration, or increased sensitivity. This is especially common among people who experience nighttime acid reflux. Proper dental care and treatment of GERD are important in preventing further damage.
While not a direct complication of GERD itself, long-term untreated GERD can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. The constant irritation and inflammation caused by stomach acid may lead to changes in the cells lining the esophagus, which can eventually develop into cancerous cells. Regular monitoring and treatment of GERD are crucial in preventing this potential complication.
GERD can also significantly impact a person’s daily life, causing discomfort and pain that may interfere with their work, sleep, and overall well-being. Constant heartburn or chest pain can be disruptive to one’s daily routine and affect their quality of life. Seeking proper treatment for GERD is essential in managing these symptoms and improving overall health and well-being.
As you can see, GERD is not just a simple case of occasional heartburn or acid reflux. If left untreated, it can lead to various complications that can significantly impact one’s health and daily life.
There are some steps you can take to prevent or minimize your risk of developing GERD, such as:
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms associated with this condition, it is important to speak to your GERD specialist as soon as possible. They can provide advice on treatment options and lifestyle changes which could help reduce and manage the condition. Taking steps to reduce the risk factors is also recommended, such as quitting smoking or reducing alcohol intake. Furthermore, eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day, avoiding trigger foods and keeping a healthy weight may all help with managing GERD.
Helpful lifestyle changes like these, alongside appropriate medical treatment, can help ensure that esophageal cancer does not develop due to long-term untreated reflux. If you think that you may be at risk of developing esophageal cancer because of chronic GERD, it is important to speak to your doctor right away. They can help you find the best treatment plan from medication to surgery, and lifestyle changes that are tailored to suit you and your individual needs.
If left untreated, reflux can also lead to esophageal cancer. Therefore, it is important to speak to a doctor if you experience symptoms such as heartburn or acid reflux on a regular basis in order to reduce the risk of developing esophageal cancer. Taking proactive steps like reducing risk factors for acid reflux and adopting helpful lifestyle changes could be beneficial for managing your condition and protecting your health.
Understand endoscopic surgery: what it entails, the procedure, benefits, and...
Understand endoscopic surgery: what it entails, the procedure, benefits, and...
Understand endoscopic surgery: what it entails, the procedure, benefits, and...
Here at KYM Surgery, we believe in providing holistic & comprehensive medical care for all patients.
Here at KYM Surgery, we believe in providing holistic & comprehensive medical care for all patients.